
- #Virtual optical disk file linux full
- #Virtual optical disk file linux software
- #Virtual optical disk file linux free
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done # ls /dev/sd*Ĭreate an ext3 file system on the new disk using the new ‘sdb’ disk from the above list of disks # mkfs -t ext3 /dev/sdb Log into the Virtual machine using the root credentials and run this command. After adding the Hard disk to VMware/vSphere/vCenter it looks like this. In the vSphere Client inventory, right-click the virtual machine and select Edit Settings.Ĭomplete the wizard. Log into the vCenter Server using the vSphere Client. Run this below command and make note of the sdx entries, means list of existing hard disks. To add a new virtual disk for an existing Linux virtual machine, Log in as root on your Linux virtual machine.
#Virtual optical disk file linux full
For a full description of the utilities mentioned in this article, please refer to the manuals. We are assuming that you are already familiar with Linux system administration skills and having knowledge of vCenter Server or vSphere Client. Here are some steps for adding a new SCSI based virtual disk on a CentOS Linux virtual machine.
#Virtual optical disk file linux free
You should see the newly created unassigned free space.This article helps you to create and add a new virtual disk to an existing Linux virtual machine on VMware. Resize the disk to 12,000MB with the following command: VBoxManage.exe modifyhd "C:\Users\StephanA\VirtualBox VMs\Fedora_33\Fedora_33.vdi" -resize 12000īoot the virtual machine and open the Disks utility. If your host system is running Windows, open a command prompt and navigate to C:\Program Files\Oracle\VirtualBox. To increase the filesystem's space within the virtual machine, you must first increase the virtual hard drive on your host system. Luckily, I chose to use LVM, so I can easily fix this mishap.
#Virtual optical disk file linux software
Don't open the GNOME Software center or anything else that might download files from the internet in this condition.
A fresh installation with no additional software (except the VirtualBox Guest Additions) takes nearly the whole 8GB of available space. Then assign the downloaded Linux distribution image you want to install:Īs I mentioned, a disk space of 20GB is recommended, and 8GB is the absolute minimum for a Fedora 33 installation to boot up.

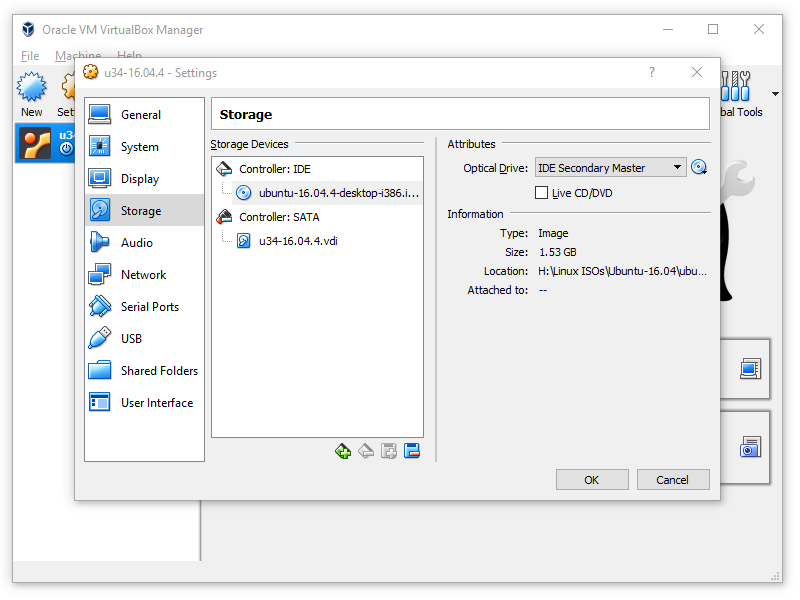
Click on the CD icon on the right, and select Choose a disk file…. Navigate to Storage and select the virtual optical drive.
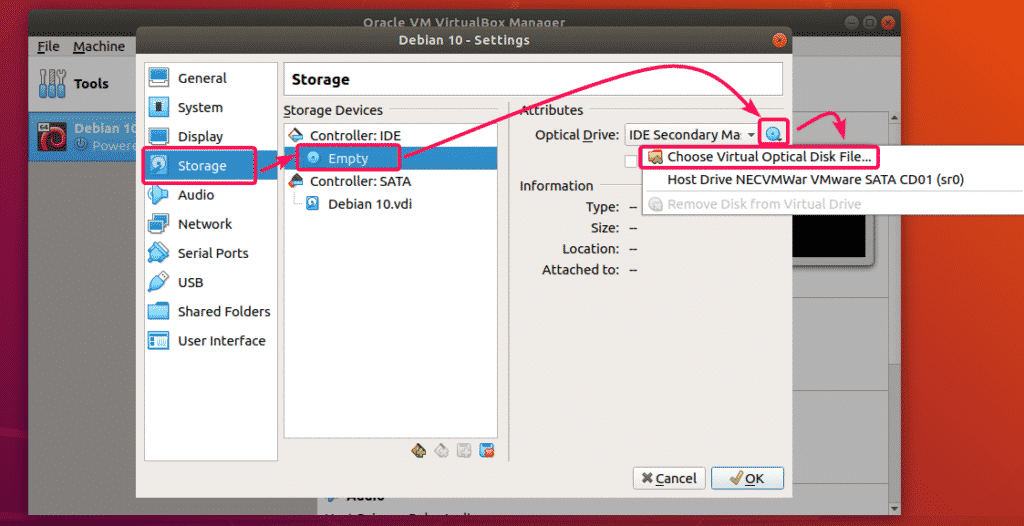
It does not matter if it's a 32-bit or 64-bit OS image.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
